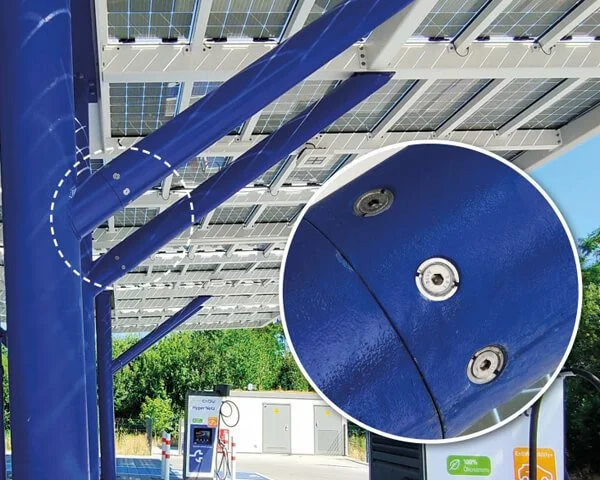
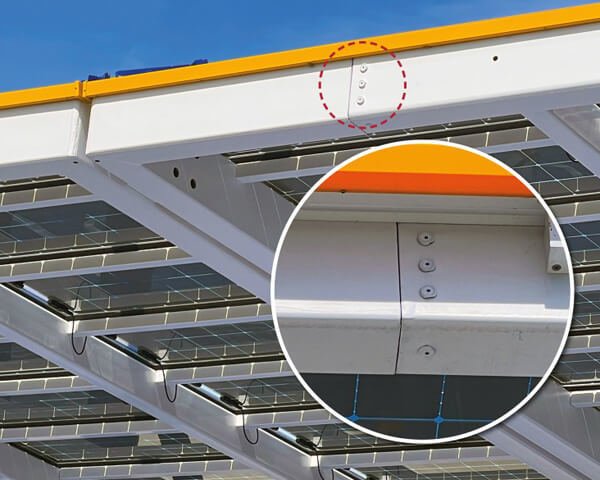
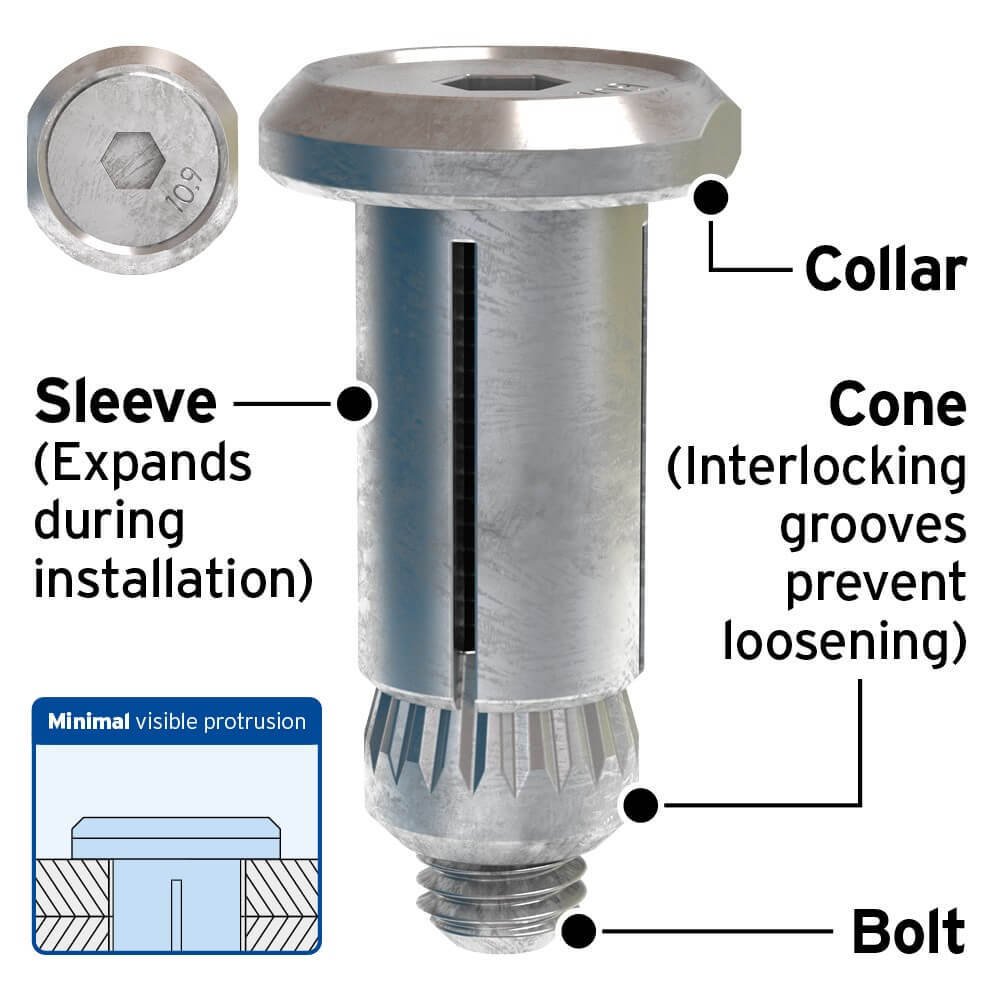
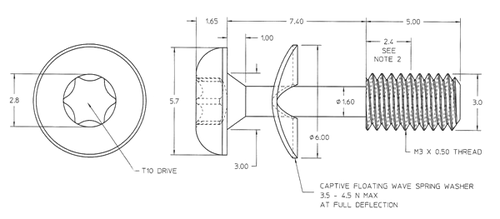
What is a tension control bolt?
A tension control bolt, also known as a tension-controlled bolt or a TC bolt, is a type of mechanical fastener that is designed to be tightened to a specific tension. It is used in a variety of applications where the correct level of tension is critical, such as in the construction of bridges, towers, and other structures. The bolt is tightened using a torque wrench or other tool, and the tension is measured using a special device called a tension meter. The bolt is tightened until it reaches the desired tension, and then it is secured in place using a locking mechanism. This helps to ensure that the bolt remains at the correct tension and does not loosen over time.
When should tension control bolts be used?
Tension control bolts are typically used in applications where the correct level of tension is critical to the performance of the structure or the safety of the people using it. Some examples of when tension control bolts might be used include:
In the construction of bridges, towers, and other large structures, where the bolts are used to hold various components together and help to distribute loads evenly.
In the construction of buildings and other structures, where the bolts are used to hold together structural elements such as beams and columns.
In the manufacturing of heavy machinery and equipment, where the bolts are used to hold together various components and ensure that they are properly aligned.
In any application where a high level of tension is required, such as in the construction of offshore platforms or in the mining industry.
Overall, tension control bolts are used anytime it is important to maintain a specific level of tension in a bolt in order to ensure the safety and integrity of a structure or machine.
Are there any downsides to using tension control bolts?
There are a few potential downsides to using tension control bolts:
Cost: Tension control bolts are generally more expensive than standard bolts, as they require more precise manufacturing and are typically made from higher-grade materials.
Complexity: Using tension control bolts requires specialized tools and equipment, such as a torque wrench and a tension meter, and may require additional training to use correctly.
Installation time: Installing tension control bolts can be time-consuming, as the bolts must be tightened to the correct tension using a torque wrench or other tool, and the tension must be carefully measured using a tension meter.
Maintenance: Tension control bolts may require more frequent maintenance and inspection than standard bolts, as the tension must be monitored and adjusted as needed to ensure that it remains at the correct level.
Overall, while tension control bolts offer many benefits in certain applications, they may not be the most practical choice in all cases due to the additional cost and complexity involved.
If you’d like more information about tension control bolts, contact Mudge Fasteners at (800) 634-0406.